Space sustainability
Find answers to questions about space debris, the risk to satellites in orbit, and how space sustainability can help, as well as the UK Space Agency's work to address these issues.

A view of London from Greenwich observatory. The sky becomes black space at the top of the image where space debris can be seen orbiting Earth above London.
Join the WatchSustainable
aSpace videoCommunity byHub
UKSustainable Space AgencyCommunity aboutHub spaceto sustainability.
Watchstay aup videoto aboutdate howwith all the UKlatest Spacenews Agencyand isactivities communicatingin space sustainability. Members can help shape the importancedevelopment of spacestandards, sustainabilityaccess tokey thefunding nextupdates, generation.share best practice and common challenges, and connect with like-minded experts in this field.
ISAM Conference 2025

The ISAM Conference will be held on 4-6 June 2025 at the ICC Belfast.
The 2025 ISAM Conference will be held on 4-6 June 2025 at the ICC Belfast.
To find out more about the ISAM Conference 2025 and register for updates about sponsorship, exhibiting and speaking, visit the ISAM Conference website.
Watch a video by the UK Space Agency about space sustainability.
Introduction
Space plays an increasingly crucial role in our daily lives, and the issue of space debris looms large on the horizon. Imagine a scenario where everyday services like TV, navigation, weather forecasting, and online banking are disrupted due to a satellite collision. This is a rising concern and why the UK government is taking bold steps to mitigate the risks associated with space debris by investing in national capabilities and international cooperation.
Scale of the debris challenge
Statistical models estimate that there are approximately 40,500 space debris objects measuring more than 10 cm in orbit; 1.1 million objects measuring between 1 cm and 10 cm, and a staggering 130 million more pieces measuring between 1 mm and 1 cm in orbit. Of these, almost 37,000 objects are actively tracked and catalogued. These include relics of the past such as old satellites, spent rocket bodies, and fragments from previous collisions.
Risk to active satellites
Active satellites that provide vital services here on Earth are at risk of collision with other satellites and the huge quantity of human-made debris in orbit around our planet which is why we work to promote the responsible use of space. This is very wide ranging and achieved through a combination of regulation, development of sustainability standards, technological advancements, missions like debris removal, and robust surveillance and tracking services that provide timely warnings for satellites in imminent danger as well as warnings if debris is predicted to fall on UK territory.
UK commitment to tackling space debris
The UK, in accordance with the National Space Strategy, is ramping up its efforts in space sustainability. This includes two studies, awarded to Astroscale and ClearSpace, towards a national active debris removal (ADR) mission.
Phase B mission studies were awarded in September 2022, totalling £5.3 million, with preliminary design reviews successfully completed by both companies in April 2024. A further £4.7 million has recently been awarded to develop the next phase which will further develop and derisk the key technologies required and provide a comprehensive understanding of the risks and costs involved.
These will help the UK Space Agency decide which concept to take forward to a fully-fledged design and launch phase, culminating with a national mission to demonstrate UK capability to rendezvous, dock with, and deorbit two defunct UK-licensed satellites.
Astroscale: Securing Space Sustainability
In 2013, Astroscale’s CEO and Founder, Nobu Okada, made a promise to himself that he would find a solution to the space debris issue by the end of 2020. A decade on, over 600 people – from engineers and mission operators to project managers and support staff – have joined Nobu on his quest, working in the UK, France, Israel, the USA and Japan. With solutions ranging from managing satellites that have reached the end of their life, to removing large space debris objects, to future refuelling and recycling services, Astroscale is developing innovative and scalable solutions to enable a circular economy in space. A first mover in the rapidly growing in-orbit servicing industry, Astroscale is blazing a trail towards a safer space environment for future generations.
The UK Space Agency is funding Astroscale to continue developing its technology and capability to remove unprepared inactive satellites from low Earth orbit. The Cleaning Outer Space Mission through Innovative Capture (COSMIC) will harness Astroscale’s rendezvous and proximity operations and robotic debris capture capabilities to remove two defunct UK satellites currently orbiting Earth.
Watch a video about the COSMIC mission.
Visit Astroscale’s website to find out more, or their Careers page for opportunities to join the team.
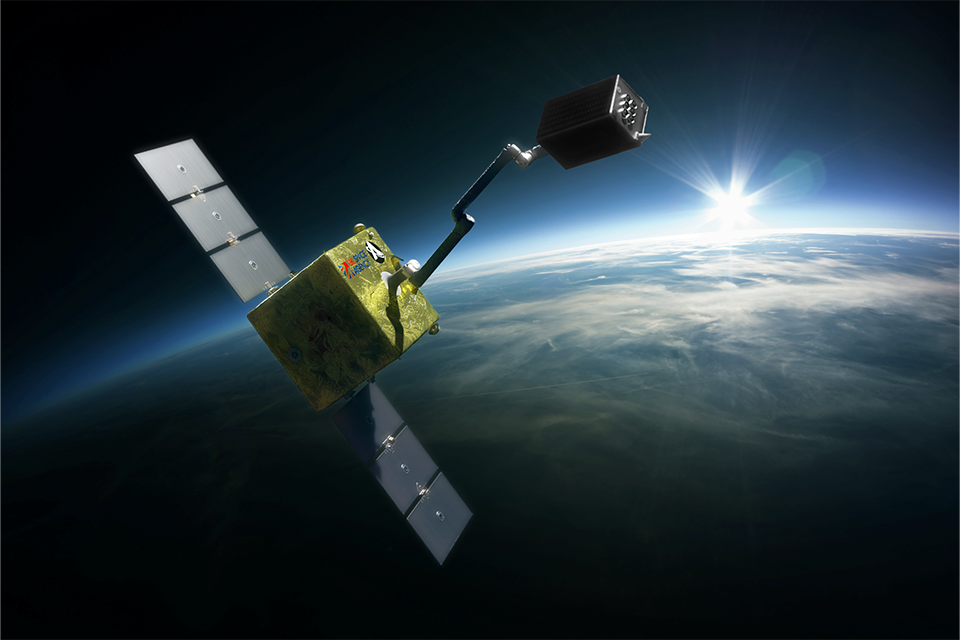

An artist's impression of the Astroscale COSMIC mission in operation. Image: Astroscale
ClearSpace: Revolutionising Space Missions
Founded in 2018, ClearSpace is on a mission to revolutionise space missions. With dynamic engineering teams spread across their offices in Switzerland, the UK, Germany, Luxembourg, and the United States, ClearSpace is developing technologies that span the gamut of in-orbit servicing applications. From disposal and in-orbit transport to inspection, assembly, manufacturing, repair, and recycling, ClearSpace aims to usher in a new era of sustainable space operations and foster a circular space economy.
ClearSpace has been selected by the UK Space Agency to develop an Active Debris Removal mission capable of removing multiple dangerous objects from space. The Clearing of the LEO Environment with Active Removal (CLEAR) mission, which will advance key technology building blocks, is a catalyst for the development of commercially viable disposal services.
Watch a video about the ClearSpace CLEAR mission.
Visit the ClearSpace website to find out more about its efforts to combat space debris with the CLEAR mission. Visit their Careers page for opportunities to join the team.
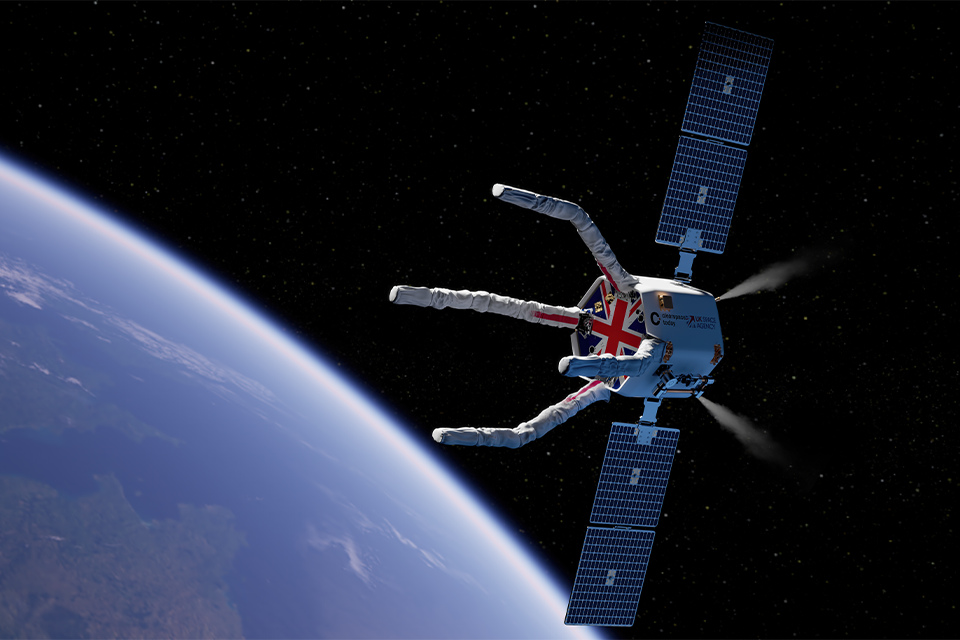

An artist's impression of the ClearSpace CLEAR mission in operation. Image: ClearSpace
What else are we doing about space sustainability?
We take a multi-faceted approach to delivering on our space sustainability commitments, investing heavily in both European Space Agency (ESA) and national initiatives. Alongside debris removal and in-orbit servicing and manufacturing, we have teams working in areas such as space surveillance and tracking, regulation and standards, and, crucially, international cooperation.
Through ESA’s space safety programme, we are a major investor in the ClearSpace-1 mission to remove a piece of debris from orbit, and lead nation on the important space weather monitoring mission, Vigil. Through ESA’s Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems (ARTES) programme, we have supported an initiative led by Astroscale and partnered with OneWeb, to remove a non-operational telecommunications satellite which may prove a hazard to future orbital operations.
Refuelling
The UK Space Agency is funding research into refuelling an upcoming mission to remove space debris, which could help prolong the life of satellites and prevent adding more debris to the space environment.
We launched 4 feasibility studies totalling £2 million, led by Astroscale, ClearSpace, Orbit Fab and Thales Alenia Space, to demonstrate the ability to refuel a UK national debris removal mission and look at opportunities for refuelling a commercial satellite. These studies will complete in late 2024.
Atmospheric Ablation Studies
The potential effects of de-orbiting many objects into Earth’s upper atmosphere are not well understood.
The UK Space Agency is funding a detailed review of existing research on atmospheric ablation which will then guide the scope and type of focused research required to aid decision-making on this important issue.
This will then be used to inform policy for In-Orbit Servicing, Assembly & Manufacturing and Active Debris Removal activity in Low Earth Orbit.
Space surveillance and tracking
In May 2024, the UK Space Agency and Ministry of Defence launched a National Space Operations Centre (NSpOC) which combines and coordinates civilian and military Space Domain Awareness (SDA) capabilities to enable operations and protect UK interests from space-related threats, risks and hazards.
ISAM Test Facility upgrades
The UK Space Agency is funding work which aims to prolong the life of satellites, as part of efforts to ensure space remains sustainable for future generations.
The package includes a £2 million upgrade to the Satellite Applications Catapult’s In-orbit Servicing, Assembly and Manufacturing (ISAM) test facility at the Westcott Space Cluster in Aylesbury. The facility will provide unique capabilities in the UK where companies can verify, validate and demonstrate a range of in-orbit operations including manufacturing, servicing, inspection, repair and assembly.
To find out more about the facility’s upgrade, please visit their website.
Regulation and standards
Safe, secure and sustainable practices require an agreed set of rules, regulations and guidance. These help maximise access to an environment whilst minimising the burden placed on it and its users – this is true for every environmental domain on earth (maritime, land and air), and applies equally to space. Novel and innovative operations that break the traditional mould of launching into an orbit around our planet mean we need to evolve our regulatory environment.
We launched a Consultation on Orbital Liabilities, Insurance, Charging and Space Sustainability. This looks at policy initiatives on liability, insurance and charging for licence fee applications which incentivise the adoption of more sustainable practices.
The consultation also covers actions the UK is taking on sustainability, as well as looking at questions on longer-term sustainability to help inform thinking. This includes a proposal to develop a longer-term sustainability roadmap and work to develop a set of space sustainability principles (the Earth∞Space Sustainability Initiative).
International cooperation
Space is global – there are no borders – so working together effectively at the national and international level is crucial to ensure coherence and alignment.
The primary, multilateral forum for international engagement is the UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) which decides the future of global and commercial space regulation. The UK has an excellent reputation and plays a strong role at COPUOS, allowing us to drive forward the agenda on key issues relating to space and sustainability. The UK is also funding a number of initiatives through the UN Office of Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) to promote understanding and adoption of the Long-Term Sustainability Guidelines, as well as wider capacity building on space regulation.
Conclusion
In the new era of space exploration, the UK is taking bold steps towards a cleaner, more sustainable future in space. These efforts promise a brighter and more secure space environment for generations to come. As we journey deeper into the cosmos, we must all embrace this opportunity for progress and innovation, ensuring a legacy of responsible space stewardship that will benefit future generations.
Contacts
We love talking about space sustainability. To find out more, or to be added to our newsletter, please contact us here:
UK Space Agency: sustainability@ukspaceagency.gov.uk
Astroscale: media_asuk@astroscale.com
ClearSpace: media@clearspace.today
Updates to this page
Last updated
-
Information about the Sustainable Space Community Hub added to the landing page. Order of content on the landing page updated.
-
Added information on 2025 ISAM Conference.
-
Updates to content throughout the page.
-
A video about space sustainability has been added to the top of the page.
-
Updated information about the IOSM Conference on the landing page.
-
Added IOSM content and updated content throughout the page.
-
First published.
Update history
2025-01-06 14:39
Information about the Sustainable Space Community Hub added to the landing page. Order of content on the landing page updated.
2024-12-18 14:25
Added information on 2025 ISAM Conference.
2024-10-11 15:21
Updates to content throughout the page.
2024-09-16 15:51
A video about space sustainability has been added to the top of the page.
2024-07-10 13:07
Updated information about the IOSM Conference on the landing page.
2024-05-03 16:23
Added IOSM content and updated content throughout the page.
2023-10-07 08:30
First published.