16 to 19 funding: how it works
An overview of the 16 to 19 funding formula.
For information
This page provides an overview of how we calculate 16 to 19 funding. The first 2 sections provide general information about this page and the guidance we have available. The following sections provide information on all elements of the 16 to 19 funding formula.
We have published information for 16 to 19 funded institutions on how funding will work in academic years 2021 to 2022 and 2022 to 2023.
The section on additional funding elements has guidance on:
- high needs funding
- care standards
- student support
- teachers’ pension scheme grant
You can find further information on our main collection page for funding education for 16 to 19 year olds and in our published funding guidance.
New for 2022 to 2023
On 27 October 2021, the Chancellor of the Exchequer announced a three-year spending review outcome for 16 to 19 education, making available an extra £1.6 billion in 2024 to 2025 financial year compared with 2021 to 2022. This is in addition to the £291m for 16 to 19 education in 2021 to 2022 and the £400m that the government provided in 2020 to 2021.
Summary
We fund sixth-form colleges, further education (FE) colleges, sixth-forms in schools, sixth-forms in academies, special schools, special academies, independent learning providers (ILPs), local authorities (LAs), special post-16 institutions (SPIs) and some higher education institutions (HEIs). We fund these institutions to provide study programmes for young people.
We fund:
-
students aged 16 to 19
-
students up to the age of 25 when they have an education, health and care (EHC) plan
-
14 to 16 year-olds who are directly enrolled into eligible FE institutions
-
home educated students of compulsory school age at any FE college
We use a national funding formula to calculate an allocation of funding to each institution, each academic year. We fund special schools and special academies using place numbers only. We do not use the national funding formula for these institutions.
We calculate the basic funding for institutions using national funding rates, which depend on the size of their students’ study programmes. These rates are regardless of which type of institution they study at or what they study. We then apply the other elements of the funding formula, as described below. To attract funding, a student must meet the published eligibility criteria, such as residency requirements. These are set out in the funding regulations guide for the appropriate academic year. Students must stay on their study programmes for a certain amount of time to qualify for funding. Further information about qualifying periods is available in the student numbers section.
Funding formula and study programmes
The funding formula funds institutions to deliver study programmes to their students. At enrolment, the institution and the student agree what each student is going to study. A learning agreement/timetable is drawn up showing what the study programme is and the qualification and non-qualification planned hours that make up the study programme.
The study programme must be tailored to the prior attainment of each student, have clear study and/or employment goals reflecting the student’s prior attainment, show progression in learning, and should include:
-
substantial qualifications or work experience
-
maths and English for students who have not achieved grade 9 to 4, A*-C GCSE in these subjects by age 16
-
high-quality work experience
-
added value non-qualification activity
Most study programmes have a core aim. The core aim of a study programme is either a substantial qualification which can be academic or vocational, or work experience. It will usually be the component with the largest amount of timetabled activity associated with it. Study programmes can only have one core aim at a time. Core aims are an essential part of the funding allocations calculation.
How the funding formula works
We use a funding formula to calculate institutions’ allocations each academic year. There are several elements within the funding formula that make up the core programme funding, total programme funding and overall total funding. The diagram below shows the elements of the funding formula.
Figure 1: 16 to 19 funding formula
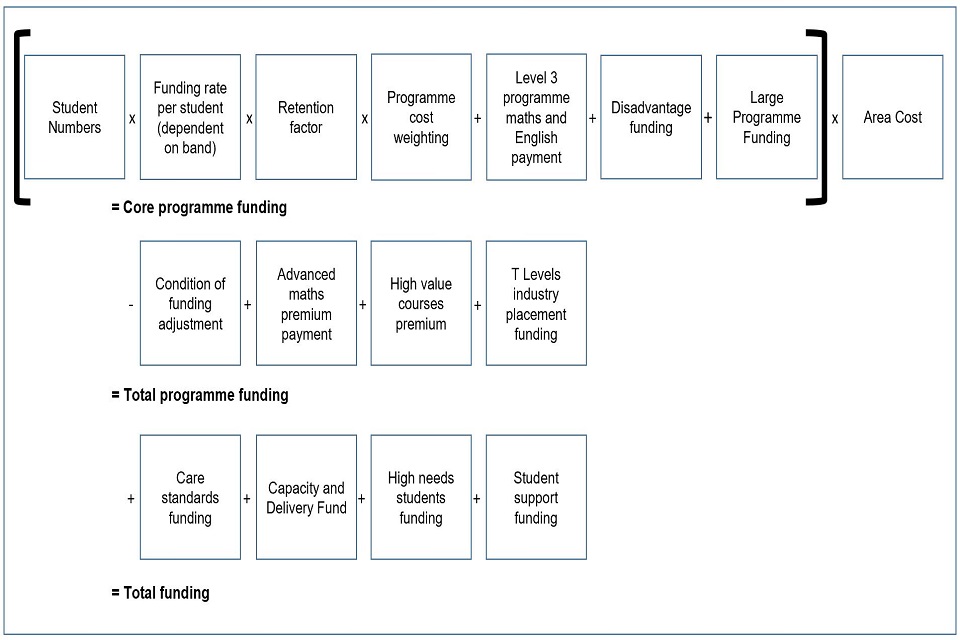
Core programme funding includes the following elements multiplied together:
-
student numbers
-
funding rate per student (dependent on funding band)
-
retention factor
-
programme cost weighting
with the following elements then added to that figure:
-
level 3 programme maths and English payment
-
disadvantage funding
-
large programme funding
and the total multiplied by:
- area cost
Total programme funding includes the following elements:
-
condition of funding adjustment (subtracted) plus
-
advanced maths premium payment
-
high value courses premium
-
T Levels industry placement funding (all added)
Total funding includes the following elements (all added):
-
care standards funding
-
capacity and delivery fund
-
high needs students funding
-
student support funding
You will find a full description of each element within the funding formula and how they are used on this page.
The data used to calculate each element is taken from data returns submitted by institutions. This information is mainly collected via the individualised learner record (ILR), for FE institutions, and the autumn school census, for schools and academies. Institutions are required to submit regular and accurate data returns to the department.
For FE institutions, both the Funding Information Service (FIS) and Submit Learner Data provide ESFA funding reports. This enables institutions to check their data is accurate.
We created the post-16 interactive school census tool to help schools and academies submit accurate autumn census returns. This interactive tool also provides information on how we use the data returned in the autumn census to calculate funding for schools and academies. 16 to 19 funding reports are available in COLLECT throughout the Autumn census returns window. We also publish 16 to 19 funding reports guidance within the school census user manual.
For 16 to 19 institutions we provide an allocation calculation toolkit (ACT) before the final allocation statements have been issued. This toolkit demonstrates to institutions how we have used their data and the various elements of the funding formula for their organisation. We also publish explanatory notes to guide institutions through their revenue funding allocation statement. We will publish these when statements are released.
Further information is in the funding regulations guide and the rates and formula guide.
Programme funding: core elements
We have published more information about these core elements in the relevant sections of the funding rates and formula guidance.
Funding Rates
We determine the funding rate for each student by the size of their study programme based on their planned hours.
We fund all 16- and 17-year-old full time students at the same national funding rate per student, per year. The funding rate can vary between academic years.
Funding rates are set out in the national funding rate sections of the guidance for the academic years 2021 to 2022 and 2022 to 2023.
The guidance also contains information on how we decide student numbers for:
-
new institutions
-
closing institutions
-
institutions transferring provision from one to another
-
institutions who are increasing the number of students (in-year growth)
-
merging institutions
Other elements of core programme funding
These elements of the funding formula use historic data based on the latest full year. We have published a summary of what data we will use for 16 to 19 allocations for 2022 to 2023.
Where there is no historic data, for example for new institutions, we use averages for a similar type of institution.
Retention
Retention means whether a student completed their programme (were retained) or withdrew/dropped out. The retention factor gives institutions less funding to compensate for students who had less delivery and therefore who incur less cost.
More information on retention criteria and funding for withdrawing students is described in the 16 to 19 funding information.
Programme cost weightings
Programme cost weightings (PCWs) provide an uplift for subjects that cost more to deliver. PCWs are determined by the core aim’s sector subject area (SSA) tier 2 classification.
A list of PCWs is given in the funding rates and formula guidance for the relevant year.
Level 3 programme maths and English payment
This additional maths and English funding is provided to support the delivery of maths and English to those students on substantial level 3 study programmes (including T Levels) who have not yet attained a grade 9 to 4 GCSE or equivalent in either or both of these subjects.
Students who have not yet attained a grade 9 to 4 GCSE or equivalent in maths and/or English will attract:
- a single £750 payment per subject for a 2-year programme or
- a single £375 payment per subject for a 1-year programme
Allocations for this payment are based on full-year ILR or School Census data.
We have published further information about how the payment is calculated.
Disadvantage funding
Disadvantage funding is made up of 2 blocks: one to account for students’ economic deprivation, and one to account for low prior attainment in English and maths. Disadvantage funding is not separated and providers are free to choose the best ways to use this additional funding to attract, retain and support disadvantaged students and those with learning difficulties and disabilities.
Large programme uplift element
Large programme funding supports students who take much larger study programmes in order to prepare for work and university. It gives providers the ability to stretch their most able students by offering a broad range of qualifications.
Area cost uplift
The costs of delivering education in London and the South East are higher than the rest of England. Institutions in these parts of England get additional funding through the area cost uplift.
Programme funding: additional elements
We have published more information about these additional elements in the relevant sections of the funding rates and formula guidance.
Maths and English condition of funding
We give extra funding to providers to deliver maths and English to students doing substantial level 3 study programmes or T Levels.
Advanced maths premium
The purpose of the advanced maths premium is to support the sector to grow the number of students studying high quality maths qualifications to level 3. The funds can be used to provide whatever support a provider deems necessary to do this.
We are continuing to fund the advanced maths premium in 2022 to 2023. We give providers additional funding to increase the number of students studying for certain advanced maths qualifications.
High value courses premium
The high value courses premium is additional funding to encourage and support delivery of selected substantial level 3 study programmes (including T Levels) in selected A level subjects or Sector Subject Areas (SSAs) that lead to higher wage returns. Providers will receive £400 per eligible student per year. We have published full eligibility and payment details on GOV.UK.
T Levels Industry Placement funding
Industry Placements are a compulsory element of the T Level. Placements are to be delivered in line with the published standards and principles. We will fund Industry Placements at £275 per student for each of the 2-years of the T Level. Payments will be allocated for the T Level student numbers agreed with providers.
Where a provider also has an allocation of the Industry Placement Capacity and Delivery Fund (CDF) a corresponding reduction will be made to the number of students funded through the CDF. For example, a provider with 100 places funded through the CDF and an allocation of 40 T Level students will be allocated placement funding for the 40 T Level students in their mainstream allocation and 60 places through CDF.
Additional funding elements outside the programme funding formula
We calculate some elements of 16 to 19 funding outside the formula.
Care standards
Care standards (residential) funding is for those institutions who have residential accommodation for students under the age of 18. The Care Standards Act 2000 puts extra responsibilities on these institutions, and these mean higher costs.
The funding rates and formula guide provides more information about Care Standards and how it is calculated.
Capacity and delivery funding (CDF)
The industry placement CDF helps institutions prepare to deliver substantive industry placements for students on vocational and technical study programmes at levels 2 and 3. The eligibility criteria may change in future years to line up with developing T Level policy. The funding for industry placements is a rate per student payment.
The funding is additional to the mainstream allocation, which already funds work experience for all students through the planned hours for employability, enrichment and pastoral (EEP) activity.
More information on CDF is available on GOV.UK.
High needs funding
High needs students (HNS) receive element 2 and 3 funding. 16 to 18 high needs students will often have an have an EHC plan or a statement of special educational needs (SEN). 19 to 25 high needs students will always have an EHC plan. HNS funding has 3 parts:
-
Element 1 – programme funding
-
Element 2 – additional education support funding: £6,000 per high needs student
-
Element 3 – top-up funding: additional funding provided on a per-student basis by their local authority
We have published more information in the high needs funding arrangements guidance.
Student support
Help is available to young people in education via a range of student support schemes.
Teachers’ pensions scheme employer contribution grant payments
We have published guidance for further education providers about the teachers’ pension scheme employer contribution grant payments.
Qualifications funded for 16 to 19 year olds
We fund qualifications that meet the following criteria:
-
they must be offered by an awarding organisation that is recognised by Ofqual
-
they must be approved for delivery by being included in the ESFA list of qualifications approved for funding: 14 to 19 (formerly known as Section 96)
ESFA funding validity for ESFA funded qualifications and eligible work experience activity on the Learning Aims Reference Service (LARS). Qualifications approved for teaching to 16 to 19 year olds that meet the maths and English condition of funding are also in LARS.
Activity that is not part of a qualification can be funded. The planned hours for that activity in the study programme can be counted for funding purposes as non-qualification activity.
Home educated (EHE) students and 14 to 16 -year-olds in FE and sixth form colleges
We fund EHE students for part time courses in FE institutions. If an institution recruits an EHE student for a full time course, then they are no longer home educated and the institution will need to meet the criteria for direct recruitment.
EHE students are returned in the ILR in exactly the same way as other 16+ students.
We fund 14 to 16-year-olds when they are enrolled in sixth form or FE colleges that meet certain criteria. 14 to 16-year- olds who are in a school or academy are funded from the usual pre-16 school funding allocation.
Full guidance on 14 to 16-year-olds in full-time further education is available on GOV.UK.
Last updated 28 April 2022 + show all updates
-
Updated to include information on 2022 to 2023 funding.
-
We have updated the 16 to 19 funding guide for the 2021 to 2022 academic year.
-
We have updated the page with information for the 2020 to 2021 academic year
-
A video explaining the allocations process for academic year 2019 to 2020 has been added.
-
This page has been refreshed to include guidance and information on 16 to 19 revenue funding allocations for academic year 2019 to 2020.
-
Updated dates, CCP references to ILP. Added a new section about application of retention.
-
A video explaining the allocations process for academic year 2017 to 2018 has been added.
-
General update to page to reflect current allocation year.
-
First published.