16 to 19 funding: how it works
An overview of the 16 to 19 funding.funding formula.
Applies to England
For information
This page provides an overview of how we calculate 16 to 19 funding. The first 2 sections provide general information about this page and the guidance we have available. The following sections provide information on all elements of the 16 to 19 funding formula.
We have published information for 16 to 19 funded institutions on how funding will work in academic years 2022 to 2023 and 2023 to 2024.
You can find further information on our main collection page for funding education for 16 to 19 year olds and in our published funding guidance .
New for 2023 to 2024
On 27 October 2021, the Chancellor of the Exchequer announced a three-year spending review outcome for 16 to 19 education, making available an extra £1.6 billion in 2024 to 2025 financial year compared with 2021 to 2022. This is in addition to the £291m for 16 to 19 education in 2021 to 2022 and the £400m that the government provided in 2020 to 2021.
Summary
We fund sixth-form colleges, further education (FE) colleges, sixth-forms in schools, sixth-forms in academies, special schools, special academies, independent learning providers (ILPs), local authorities,authorities (LAs), special post-16 institutions (SPIs) and some higher education institutions (HEIs). We fund these institutions to provide study programmes and T Levels for young people.
We fund:
- students aged 16 to 19
- students up to the age of 25 when they have an education, health and care (EHC) plan
- 14
14-to 16 year-olds who are directly enrolled into eligible FE institutions - home educated students of compulsory school age at any FE college
We use thea 16national to 19 funding formula to calculate an allocation of funding to each institution, each academic year. We fund special schools and special academies using place numbers only. We do not use the 16national to 19 funding formula for these institutions.
We calculate the basic funding for institutions using national funding rates, which depend on the size of their students’ study programmesprogrammes. or T Levels. These rates are regardless of which type of institution they study at or what they study. We then apply the other elements of the funding formula, as described below. To attract funding, a student must meet the published eligibility criteria, such as residency requirements. These are set out in the funding regulations guide for the appropriate academic year. Students must stay on their study programme or T Level for a certain amount of time to qualify for funding. Further information about qualifying periods is available in the student numbers section.
What’s new
We publish pages for each academic year so it’s easy to see what has changed.
Funding formula and study programmes
WeThe use the 16 to 19 funding formula tofunds fund institutions to deliver study programmes and T Levels to their students. At enrolment, the institution and the student agree what each student is going to study. TheA institutionlearning providesagreement/timetable ais learningdrawn agreement/timetableup showing what the study programme is and the qualification and non-qualification non-qualification planned hours that that make up the study programme.
The institutionstudy programme must tailorbe studytailored programmes to the prior attainment of each student, have clear study and/or employment goals reflecting the student’s prior attainment, show progression in learning, and should include:
- substantial qualifications or work experience
-
maths and English for students who have not achieved grade 9 to 4, A*
A*-Cto C GCSE in these subjects by age 16 - high-quality work experience
- added value non-qualification activity
Most study programmes have a a core aim . The core aim of a study programme is either a substantial qualification,qualification which can be academic or vocational, or work experience. TheIt core aim will usually be the component with the largest amount of timetabled activity associated with it. Study programmes can only have one core aim at a time. Core aims are an essential part of the funding allocations calculation.
How the 16 to 19 funding formula works
We use a funding formula to calculate institutions’ allocations each academic year. There are several elements within the 16 to 19 funding formula that make up the core programme funding, total programme funding and overall total programme funding. The diagram below shows the elements of the funding formula.
Figure 1: elements of the 16 to 19 funding formula

16 tothat 19make up your funding formula
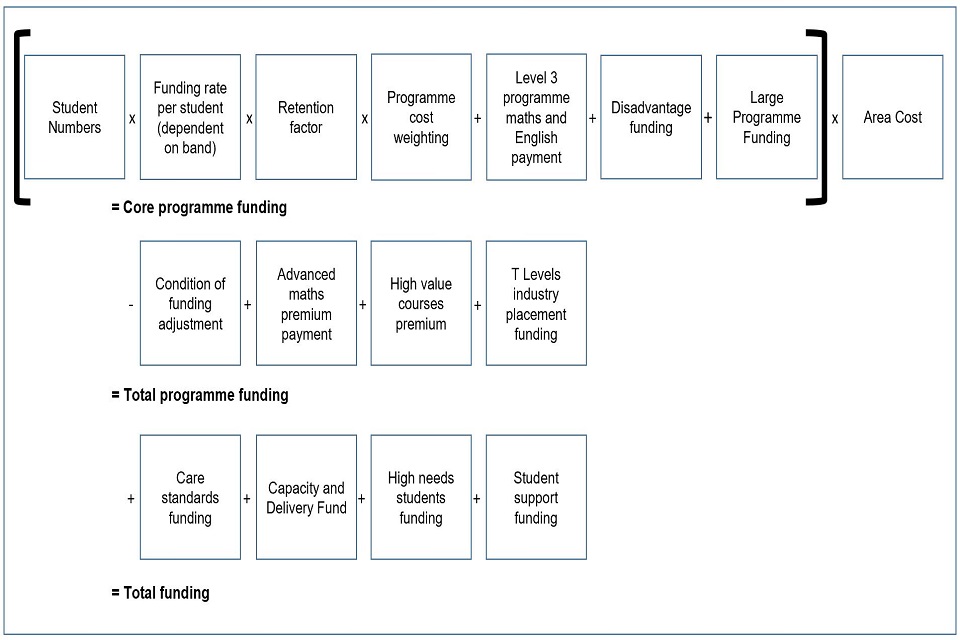
Core programme funding
To calculate,includes we take the studentfollowing numberselements andmultiplied multiply them by:together:
studentnumbers- funding rate per student (dependent on funding band)
- retention factor
- programme cost weighting
Wewith the following elements then add:added to that figure:
- English
leveland3programmeandEnglishpayment - disadvantage funding
- large programme funding
and multiply the total multiplied by:
- area cost
Total programme funding
To calculate,includes we take the totalfollowing core programme funding and:elements:
- subtract the condition of funding adjustment, then
adjustmentadd(subtracted), plus - advanced maths premium
- core maths premium
payment - high value courses premium
- T Levels industry placement funding
(alladded)
Total funding
We addincludes the following elements where(all appropriate to the total funding:added):
- care standards funding
capacityanddeliveryfund- high needs students funding
- student support funding
You will find a full description of each element within the 16 to 19 funding formula and how wethey useare themused on this page.
WeThe take the data used to calculate each element is taken from data returns submitted by institutions. This information is mainly collected via the the individualised learner record (ILR) , for FE institutions, and the autumn autumn school census, for schools and academies. Institutions mustare required to submit regular and accurate data returns to the Department for Education.department.
For FE institutions, both the the Funding Information Service (FIS) and (FIS) and Submit learnerLearner dataData provide provide ESFA funding reports. This enables institutions to check their data is accurate.
We created the the post-16 interactive school census tool for 2023 to 2024 to to help schools and academies submit accurate autumn census returns. This interactive tool also provides information on how we use the data returned in the autumn census to calculate funding for schools and academies. 16 to 19 funding reports are available in in COLLECT, the department’sDepartment for Education’s centralised data collection and management system, throughout the autumnAutumn census returns window. We also publish publish 16 to 19 funding reports guidance within within the school census user manual.
For 16 to 19 institutions, we provide an allocation calculation toolkit (ACT) tobefore supportthe final allocation statements.statements have been issued. This toolkit showsdemonstrates to institutions how we have used their data toand calculatethe various elements of the funding allocationformula for their organisation. We publish guidesalso whenpublish weexplanatory issuenotes statements toto helpguide institutions understandthrough their allocation.revenue funding allocation statement. We will publish these when statements are released.
Further information is in the the funding regulations guide and the and the rates and formula guide.
CoreProgramme programmefunding: fundingcore elements
We publishhave published more information about these core elements in the relevant sections of the funding rates and formula guidanceguidance..
We publish a table showing the data we use to calculate funding allocations for the academic year.
Where there is no historic data, for example for new institutions, we use averages for a similar type of institution.
Funding raterates
We determine the funding rate for each student by the size of their study programme or T Level based on their their planned hours.
We fund all 1616- and 1717-year-old year old full-time students at the same national funding rate per student, per year,year. where the size of programme is the same. The funding rate can vary between academic years.
WeFunding publishrates are set out in the national funding ratesrate eachsections of the guidance for the academic year:years 2022 to 2023 and 2023 to 2024.
The guidance also contains information on how we decide student numbers for:
- 2024
newtoinstitutions closing2025institutions- 2023
institutionstransferringprovisionfromoneanother institutionswhoareincreasingthenumberofstudents(in-yeargrowth)merginginstitutions
RetentionOther factorelements of core programme funding
RetentionThese meanselements whetherof athe studentfunding completedformula theiruse programmehistoric (weredata retained)based oron withdrew/droppedthe out.latest Thefull year. We have published a summary of what data we will use for 16 to 19 fundingallocations formulafor recognises2023 thatto 2024.
Where there is ano costhistoric todata, institutionsfor inexample deliveringfor programmesnew toinstitutions, studentswe whouse doaverages notfor complete.a Thissimilar istype appliedof throughinstitution.
Retention
Retention themeans retentionwhether factor,a whichstudent hascompleted thetheir effectprogramme of(were retained) or withdrew/dropped out. The retention factor gives institutions less funding withdrawnto compensate for students atwho 50%had ofless theirdelivery fundingand band’stherefore rate.who incur less cost.
WeMore explaininformation on retention criteria and funding for withdrawnwithdrawing students inis moredescribed detail in the funding16 ratesto and19 formulafunding guidanceinformation. for the relevant year.
Programme cost weightings
Programme cost weightings (PCWs) provide provide an uplift for subjects that cost more to deliver. Wedeliver. PCWs are decidedetermined a programme’s PCWs by the core aim’s sector subject area (SSA) tier 2 classification for study programmes. For T Level programmes the PCW is determined by mapping occupational specialisms to apprenticeship standards to determine the most appropriate SSA and, therefore, PCW.classification.
WeA publishlist aof PCWs is listgiven of PCWs inin the the funding rates and formula guidance for for the relevant year.
EnglishLevel and3 programme maths fundingand English payment
This isadditional amaths newand English funding elementis forprovided 2024 to 2025support academic year. In October 2023, the governmentdelivery announced an investment of £600maths millionand acrossEnglish theto nextthose 2students yearson insubstantial preparationlevel for3 thestudy Advancedprogrammes British(including StandardT (ABS).
ThisLevels) additional funding is intended to support students who have not achievedyet attained a GCSE grade 9 to 4 GCSE or aboveequivalent in Englisheither andor mathsboth toof participatethese acrosssubjects.
Students allwho studyhave programmesnot andyet Tattained Levelsa bygrade ensuring9 institutions have the resources to provide4 tailoredGCSE education or otherequivalent extrain supportmaths whereand/or neededEnglish alongsidewill qualifications.attract:
Students
adosinglenot£750needpaymenttoperbesubjectstudyingfora specific2-yearlevelprogramme oraorsingleprogramme£375topaymentattractperthissubjectfunding.forThisafunding1-yearwill replace the level 3 programme
Allocations mathsfor andthis English payment thatare wasbased specificon tofull-year ILR or levelSchool 3Census programmes.data.
We Thehave conditionpublished offurther fundinginformation appliesabout tohow all students that attract the newpayment Englishis and maths funding element.calculated.
Disadvantage funding
Disadvantage funding consistsis made up of 2 blocks: one to account for students’ economic deprivation, and one to account for low prior attainment in English and maths. WeDisadvantage dofunding is not separateseparated disadvantage funding and institutionsproviders are free to choose the best ways to use this additional funding to attract, retain and support disadvantaged students and those with learning difficulties and disabilities.
Large programme uplift element
Large programme funding supports students who take much larger study programmes in order to prepare for work and higheruniversity. education. It gives institutionsproviders the ability to stretch their most able students by offering a broad range of qualifications.
Area cost uplift
The costs of delivering education in London and the south-eastSouth East are higher than the rest of England. Institutions in these parts of England get additional funding through the area cost uplift.
Programme funding: additional elements
We have published more information about these additional elements in the relevant sections of the funding rates and formula guidanceguidance..
Maths and English condition of funding
Students doing study programmes and T Levels must study maths and/or English when they do not already hold a GCSE grade 9 to 4 (a standard pass grade) or equivalent qualification in these subjects.
This requirement is a condition of funding and we remove funding from future allocations for students who do not meet it.
Advanced maths premium
The The advanced maths premium supports supports the sector to grow the number of students studying high quality maths qualifications to level 3. InstitutionsThe funds can usebe theused funding to provide whatever support theya deemprovider deems necessary to do this.
Core maths premium
ThisWe isare acontinuing new element for 2024 to 2025.fund Thethe coreadvanced maths premium isin to2023 encourage the provision of core maths qualifications and expand maths education for students up to the2024. ageWe ofgive 18.institutions Itadditional isfunding intended to supportincrease students’ participation in programmes with core maths qualifications by ensuring institutions have the resourcesnumber to provide extra hours of educationstudents orstudying otherfor extracertain supportadvanced where needed to deliver core maths qualifications.
High value courses premium
The high value courses premium is additional funding to encourage and support delivery of selected substantial level 3 study programmes and(including T LevelsLevels) in selected A level subjects or sectorSector subjectSubject areasAreas (SSAs) that lead to higher wage returns. Providers will receive £600 per eligible student per year. We have published full eligibility and payment details on GOV.UK.
T LevelLevels industry placement funding
Industry providers should deliver placements in line with the industry placements delivery guidance.
We fund T Level providers a total of £550 per student for the industry placement element of the T Level programme, £275 per student in each of the 2 years of the T Level. We pay for the T Level student numbers agreed with institutions.
This funding is to support the infrastructure and resource required to plan, source, deliver and monitor industry placements. It is not to support employer costs for hosting placements.
Additional funding elements outside the 16programme to 19 funding formula
We calculate some elements of 16 to 19 funding outside the formula.
Care standards
Care standards (residential) funding is for those institutions who have residential accommodation for students under the age of 18. The Care Standards Act 2000 puts extra responsibilities on these institutions, and these mean higher costs.
The funding rates and formula guide provides more information about Care Standards and how weit calculateis it.calculated.
Capacity and delivery funding (CDF) - for CDF-funded providers with an Ofsted rating of ‘requires improvement’ or ‘inadequate’ only
The industry placement CDF helps institutions prepare to deliver substantive industry placements for students on vocational and technical study programmes at levels 2 and 3. The 2022 to 2023 academic year was the final year of funding for providers rated as ‘outstanding’ or ‘good’ by Ofsted. Those CDF-funded providers with an Ofsted rating of ‘requires improvement’ or ‘inadequate’ are able to access this funding for one final year in the 2023 to 2024 academic year.
The funding is additional to the mainstream allocation, which already funds work experience for all students through the planned hours for employability, enrichment and pastoral (EEP) activity.
More information on CDF is available on GOV.UK.
High needs funding
High needs funding is for institutions that have students who are assessed by the local authority in whose area they are resident as having complex special educational needs and/or disabilities (SEND), which means that the authority assesses the costs of their additional SEND support as more than £6,000 per student. Institutions will receive extra funding directly from the local authority for these students, who will often (always in the case of 1919- to 2525-year-olds) year olds) have an EHCeducation, health and care (EHC) plan drawn up by the local authority. As well as the 16normal to 19 programme funding, institutions receive:
- High needs place funding
Thisfunding, is sometimes referred to as element 2 funding. It’s paid at the rate of £6,000 per place by ESFA, from deductions made from local authorities’ high needs funding allocations, based on the basis of data supplied by authorities or ILRindividualised learning record (ILR) data, depending on the type of institution.
institution
Thisfunding, iswhich sometimes referred to as element 3 funding. This is additional funding determined on a per-student basis and paid directly by the relevant local authority, for the costs of additional support in excess of £6,000.
We have published more information in the high needs funding: 2023 to 2024 operational guide: High needs funding arrangements: 2023 to 2024.
Student support
Help is available to young people in education via a range of student support schemes.
Teachers’ pensions scheme employer contribution grant payments
We have published guidance for further education providers about the teachers’ pensionspension scheme employer contribution grant payments guidanceup forto schools and FEincluding providers.
Qualifications2022 fundedto for2023. 16We towill 19provide yeardetails olds
Weof fundthe studentsfuture toarrangements undertakeof athis studygrant programmein ordue Tcourse.
Qualifications Levelfunded thatfor contain16- to 19-year-olds
We fund qualifications meetingthat meet the following criteria:
- they must be offered by an awarding organisation that is recognised by
by - they must be approved for delivery by being included in the
theESFAfunding:14to19(formerlyknownasSection96)
Learning Aims Reference Service19
Eligible activity that is not part of a qualification can be funded. The planned hours for that activity in the study programme or T Level can be counted for funding purposes as as non-qualification activity.
ElectivelyHome home educated (EHE) students and 1414- to 16-year-olds in FE and sixth-form colleges
We fund EHE studentsfund EHE students for part-timepart time courses in FE institutions.institutions. If an institution recruits an EHE student for a full-time course, then they are no longer homehome-educated educated and the institution will need to meet the criteria for direct recruitment.
EHE students are recordedreturned in the ILR in exactly the same way as 16other to16+ 19 funded students.
We fund 1414- to 1616-year-olds year olds when they are enrolled in sixth-form or FE colleges that meet certain criteria. We14- fund 14 to 1616-year-olds year olds who are in a school or academy are funded from the usual pre-16 school funding allocation.
Full guidance on 14- to 16-year-olds in full-time further education is available on GOV.UK.
Last updated 13
-
We've updated this page to streamline the information and to include the new information for the 2024 to 2025 academic year.
-
Updated with post-16 school census tool for 2023 to 2024
-
We've updated the page for the 2023 to 2024 academic year.
-
Updated to include information on 2022 to 2023 funding.
-
We have updated the 16 to 19 funding guide for the 2021 to 2022 academic year.
-
We have updated the page with information for the 2020 to 2021 academic year
-
A video explaining the allocations process for academic year 2019 to 2020 has been added.
-
This page has been refreshed to include guidance and information on 16 to 19 revenue funding allocations for academic year 2019 to 2020.
-
Updated dates, CCP references to ILP. Added a new section about application of retention.
-
A video explaining the allocations process for academic year 2017 to 2018 has been added.
-
General update to page to reflect current allocation year.
Update history
2025-03-05 17:59
We’ve added a link to this page to the funding rates and information for 2025 to 2026. This is in the core programme funding section. We’ve made some changes to the general text to make it easier to read.
2024-02-13 14:00
We’ve updated this page to streamline the information and to include the new information for the 2024 to 2025 academic year.
2023-06-22 13:00
Updated with post-16 school census tool for 2023 to 2024
2023-03-17 14:27
We’ve updated the page for the 2023 to 2024 academic year.
2022-04-28 11:35
Updated to include information on 2022 to 2023 funding.