Tunisia
Summary
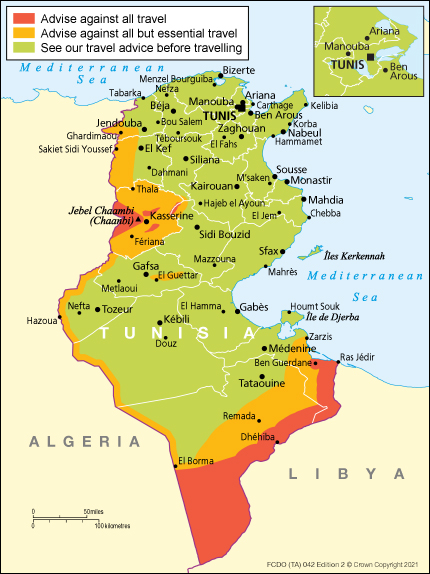
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) advise against all travel to:
- the Chaambi Mountains National Park and the designated military operations zones of Mount Salloum, Mount Sammamma and Mount Mghila
- the militarised zone south of the towns of El Borma and Dhehiba
- within 20km of the rest of the Libya border area north of Dhehiba
- the town of Ben Guerdane and immediate surrounding area
In addition and for security reasons, the FCDO advises against all but essential travel to:
- within 75km of the Libyan border, including Remada, El Borma and the town of Zarzis
- the governorate of Kasserine, including the town of Sbeitla
- within 10km of the border with Algeria south of Kasserine governorate
- within 30km of the border in El Kef and Jendouba governorates south of the town of Jendouba, including the archaeological site of Chemtou
- areas north and west of the town of Ghardimaou in Jendouba governorate, including El Feidja National Park
- within 10km of Mount Mghila
- Mount Orbata
COVID-19 entry restrictions for Tunisia
Before you travel, check the ‘Entry requirements’ section for Tunisia’s current entry restrictions and requirements. These may change with little warning. Monitor this advice for the latest updates and stay in contact with your travel provider.
Travelling from and returning to the UK
Check what you must do to travel abroad and return to England, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland.
If you plan to pass through another country to return to the UK, check the travel advice for the country you’re transiting.
If you’re planning travel to Tunisia, find out what you need to know about coronavirus in the Coronavirus section.
Following the emergence of the new strains of COVID-19, travel restrictions are evolving rapidly. Check this advice regularly or sign up for further updates.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more important than ever to get travel insurance and check it provides sufficient cover. See the FCDO’s guidance on foreign travel insurance.
For information about COVID-19 vaccines, see the Coronavirus page.
A state of emergency is in effect in Tunisia, imposed after a suicide attack on a police bus on 24 November 2015. It has been extended a number of times, most recently in February 2022.
Since the terrorist attack in Sousse in June 2015, which targeted tourists, the UK government has been working closely with the Tunisian authorities to investigate the attack and the wider threat from terrorist groups. The Tunisian government has improved protective security in major cities and tourist resorts.
Terrorists are still very likely to try to carry out further attacks in Tunisia, including against UK and Western interests. Security forces remain on a high state of alert in Tunis and other places. You should be vigilant at all times, including around religious sites and festivals. Crowded areas, government installations, transportation networks, businesses with Western interests, and areas where foreign nationals and tourists are known to gather may be at higher risk of attack. You should be particularly vigilant in these areas and follow any specific advice of the local security authorities. In more remote areas of the country, including tourist sites in southern Tunisia, security forces’ response times to an incident may vary. Follow the advice of the Tunisian security authorities and your travel company if you have one. See Terrorism
On 25 July 2021, a number of protests, some violent, occurred across the country, including in Tunis, Sousse and Sfax. Following these, President Kais Saied enacted emergency powers, including suspending the work of parliament indefinitely. Protests may occur with little or no warning. You should avoid all protests and places where crowds gather. You should be particularly cautious in areas where previous protests have occurred, including in central areas of major cities and in the vicinity of government and parliament buildings in Tunis and elsewhere in the country. You should keep up to date with developments through the media and follow instructions given by the Tunisian authorities as well as your hotel and your tour operator, if you have one. See Political situation
You can contact the emergency services by calling 197 (police - when in cities and towns), 193 (national guard - when in rural areas or small villages), 190 (ambulance) or 198 (civil protection - for assistance at incidents, such as car accidents, to provide medical assistance and response to fire).
If you’re abroad and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the nearest British embassy, consulate or high commission. Consular support may be limited in parts of Tunisia.